What Happens During a Gout Attack
Gout, or hyperuricemia, is a condition that’s caused by the long-term buildup of uric acid crystals in the bodily tissues and joints. What results from this buildup is painful inflammation that’s characterized as a type of arthritis that strikes in what’s known as a gout attack. Gout is caused by too much uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia).
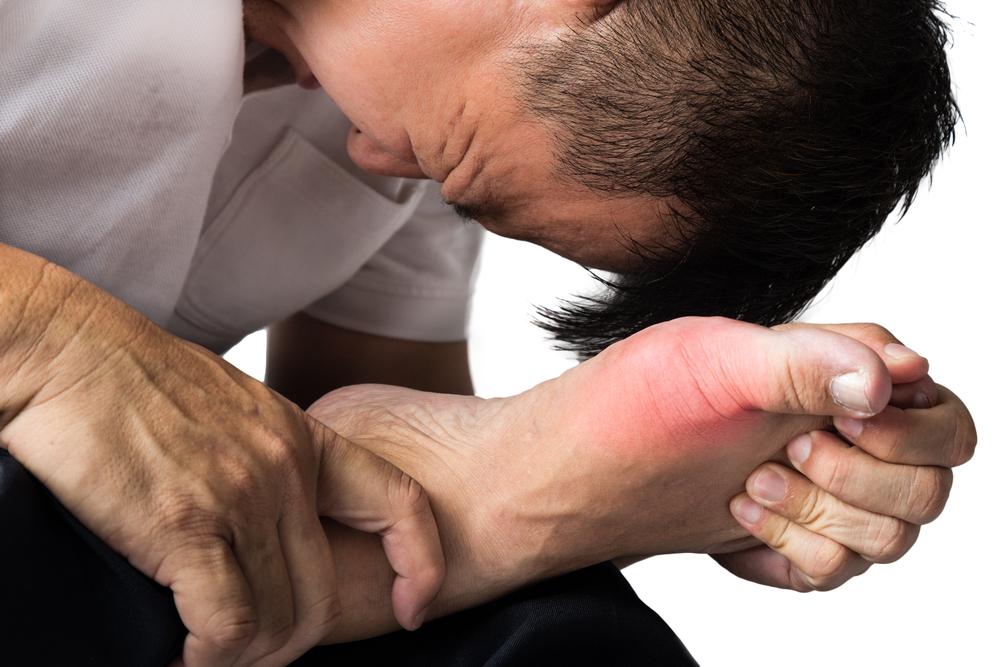
When a gout attack occurs, it’s painful due to inflammation in a joint (typically the big toe) or surrounding tissues – causing symptoms of redness, swelling, stiffness, and burning heat. Gout attacks are recurrent. Even though they will gradually subside, patients will experience them repeatedly, and they can cause permanent damage to joints and surrounding tissues if left untreated.
Many patients experiencing their first gout attack are misdiagnosed with joint sprain or tendinitis.
Gout attacks usually strike during the nighttime, with a mild pain that gradually worsens.
What’s considered a mild gout attack can cease swelling, pain, burning, redness, and stiffness after a few hours. However, patients experiencing mild gout attacks have reported symptoms lasting for up to 2 days in duration. Most mild gout attacks cease all symptoms after a week.
What’s considered a severe gout attack can leave patients with painful symptoms for up to several weeks in duration, with pain lingering for up to 1 month.
For the majority of gout patients, another gout attack often reoccurs anywhere between 6 months and 2 years after a first gout attack.
It’s important to get immediate doctor attention if you suspect you may have gout. If left untreated, the condition will only increase with severity and time.











