An Overview Of The Bone Density Test
An overview of the bone density test
The bone density test is a method to determine or measure the strength of the bone of the human body. An X-ray test called the DEXA scan is followed to determine whether the bones are fragile and likely to break. A bone density test calculates the amount of calcium and various other bone minerals available in the tested bone part.
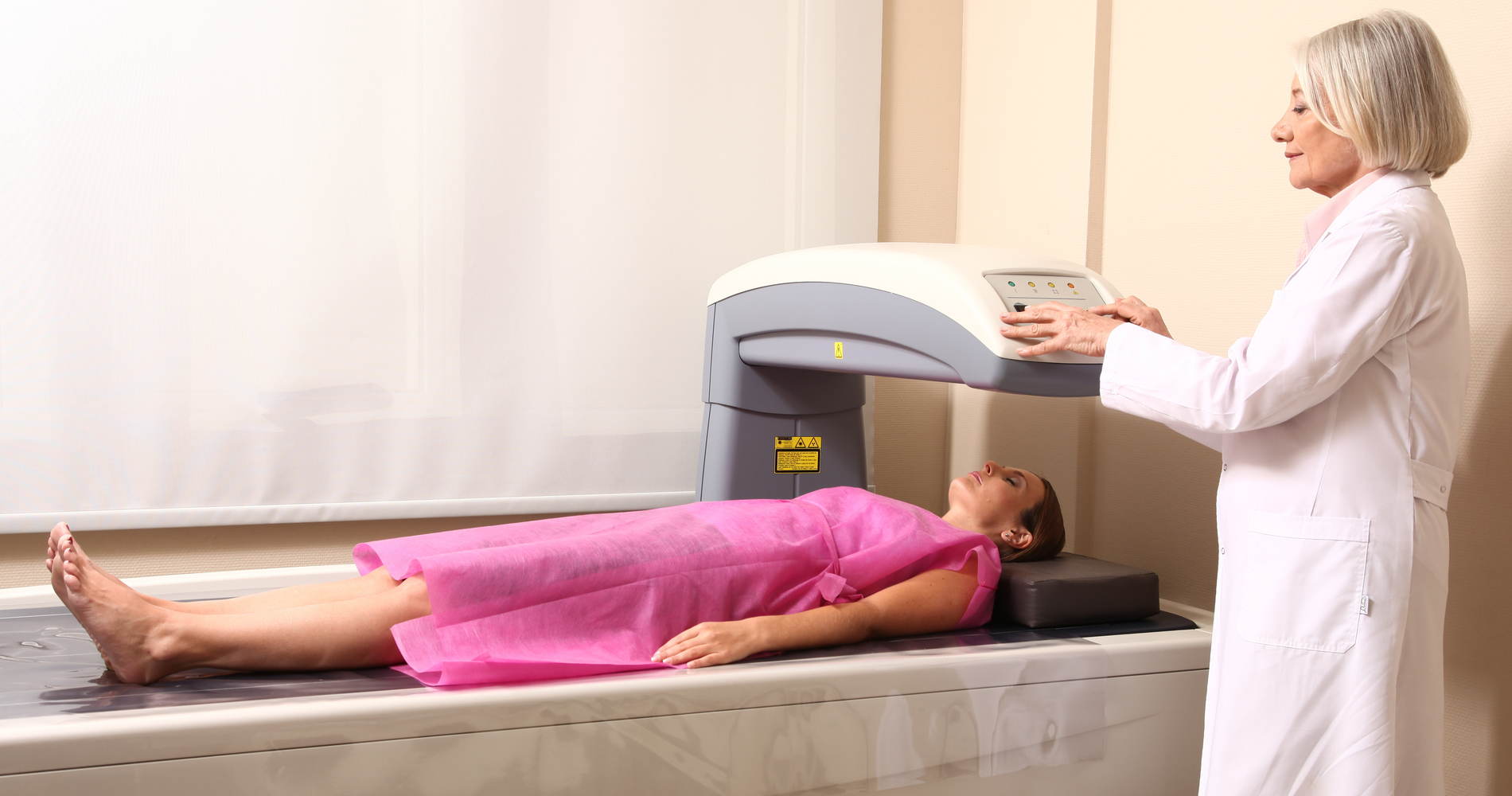
Hip, spine, and forearms are the most commonly tested bones.
Why bone density tests should be done?
You should opt to undergo a bone density test once in a few years for the following reasons:
- It helps calculate the density of particular bones and protects them from breaking by taking adequate measures in time.
- Analyzes the risk factors (such as fractures) attached to your bones.
- Helps in diagnosis and treatment monitoring of osteoporosis.
When is a bone density test recommended?
Your physician may recommend a bone density test regardless of your age and sex in case of the following:
- If you have lost height, which happens due to the fracture compression in the spine. Osteoporosis is a prime cause for this.
- If you have a bone fracture, in a normal situation, it is caused by the fragility of the bones. Such fractures can also be caused by a strong sneeze or a cough.
- You are under long-term medication, which has been the hampering the bone rebuilding process of the body.
- You underwent an organ or bone marrow transplant. This fuels a higher risk of osteoporosis due to the hampering of the bone redevelopment process for the presence of anti-injection drugs.
- You have experienced a hormone level drop.
What is the difference between a bone density test and a bone scan?
- A bone scan helps determine any specific medical issues with the bone, and it involves a special diagnostic process.
- It is primarily a nuclear radiology test involving a radioactive substance being infused into the bloodstream via an IV.
- A bone scan is used to identify various bone-related ailments such as bone tumors, infections, arthritis, fractures, bone trauma, bone cancer, and osteoporosis.
- On the other hand, a bone density test is undertaken to calculate the density of minerals available in the bones.
Who should opt for a bone density scan?
People who are from 50 to 69 years old must opt for a bone density test if they meet any of these criteria:
- Have a lower body weight
- Are alcoholic
- Are a regular smoker
- Have suffered from any minor accident resulting in the breaking of bones
- Have been consuming corticosteroid drugs for more than three months
- Are suffering from any disorders associated with osteoporosis
- Are suffering from rheumatoid arthritis
Are there any downsides of a bone density test?
- The radiation of a bone density test may affect the body adversely.
- Involvement of multiple devices increases the overall cost factor of bone density tests, and the limitation of the insurance cover becomes a burden for the patients.
- A bone density test is unable to explain the accurate cause for the low density of bones.
Is there a way to prepare for a bone density test?
- Bone density tests are painless, simple, and fast.
- It does not need any specific preparation; it can be done quickly by visiting a diagnostic center.
- Just as a precaution, inform your physician if you have any health-related complications.
How can you keep your bones stronger?
- Regular exercise is the key for stronger bones. Weight lifting is extremely good for a higher bone density. Devote thirty minutes daily to weight-bearing exercise.
- Include enough calcium in your diet. Eat food items that are high in calcium, such as leafy green vegetables and dairy products.
- Increase the intake of vitamin D; sunbathing is an easy way to facilitate this.
- Quit alcohol intake and smoking.
- Consult your physician and try to avoid drugs that affect bone density.
If you have a lower body weight or have any complications explained above; ensure that you get your bone density test done today to ensure your optimal health.











